Comedonal Acne: Causes, How To Treat It, & Ways To Prevent It
Popping is not the solution, especially when you have more appropriate treatment options.
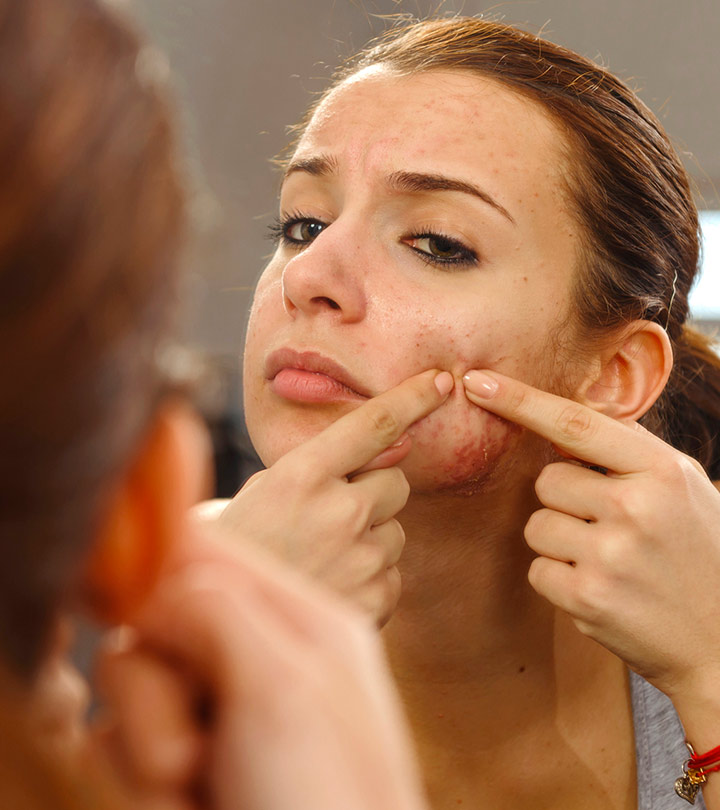

Comedonal acne is a mild form of acne. Comedones are flesh-colored bumps that later develop into pimples and more severe forms of acne. Blackheads and whiteheads are the most common examples of comedonal acne.
They are not as inflammatory or painful as other severe forms of acne. However, you still need to follow self-care practices and use topical or oral medications to manage them. Read on to learn more about them and ways to minimize them.
In This Article
What Is Comedonal Acne?
Comedonal acne is a type of acne that appears like comedones (flesh-colored small bump-like papules that mostly occur on the chin and forehead). They are pores or hair follicles plugged with oil, dirt, and dead skin cells. Blackheads and whiteheads are the most common types of comedonal acne. When the dirt and oil plugs are exposed to air, they oxidize and turn black, resulting in blackheads. When these plugs are set deeper into the pores and are white, you get whiteheads.
In the following section, we will look at the causes and risk factors of comedonal acne.
Comedonal Acne: Causes And Risk Factors
Comedonal acne is caused when the sebaceous ducts are blocked with dirt, debris, and sebum. While anyone can get comedonal acne at any point in time, certain factors increase the risk:
- Dairy (such as yogurt, milk, and cheese) consumption may cause acne (1).
- Diet with a high glycemic index/glycemic load may aggravate acne (2). Consuming foods that contain a lot of sugar and fat (such as baked goodies, junk food, and aerated drinks) may cause breakouts.
- Some believe overhydration may also cause acne. Your skin may get overhydrated due to humid conditions or from excessive use of moisturizers.
- Smoking may also cause acne and breakouts (3).
- Using excessive makeup, oily skincare products, and hair pomades may cause acne.
- Genetics may also be a factor behind comedonal acne. If it runs in your family, you are most likely to get it.
- Squeezing the existing comedones and excess use of abrasive skin products (such as scrub and chemical peels) may also aggravate your condition and cause comedonal acne.
Apart from blackheads (open comedones) and whiteheads (closed comedones), there are several other types of comedones.
Types Of Comedonal Acne
1. Microcomedones
These are the smallest comedones. They are invisible to the naked eye. They are the first stage of every blackhead, inflamed acne, or pimple.
2. Macrocomedones
These can be both open and closed comedones, but they are larger.
3. Giant Comedones
Giant comedones are large blackheads, with a diameter measuring between a few millimeters to about 2 centimeters. Older adults usually get this type of comedones.
4. Solar Comedones
These are also called senile comedones and are caused by excessive sun exposure. These can be open or closed type comedones and can be large or small. These are common in older adults.
It is very easy to identify comedones once we know what they look like.
How To Identify Comedonal Acne
Here are a few tips to identify comedones:
- They look like small fleshy bumps. The affected area feels uneven and bumpy.
- Blackheads will have a tip that appears dark brown or black. You will commonly see them on your nose.
- Whiteheads look like small whitish or flesh-colored dots on your skin.
If you have comedonal acne, there is nothing to worry about. There are plenty of treatment options to manage them. In the next section, we have discussed these in detail.
How To Treat Comedonal Acne
1. Topical Treatment
Topical treatments are readily available as OTC medicines. However, you need to know the right percentage of the ingredients that will work for your condition. Consult a doctor before trying out any topical treatment. These are available in the form of gels, creams, and face washes. The most common ingredients used for treating comedonal acne are:
Stronger retinoids need to be prescribed by a doctor. This is because using the wrong percentage of retinoids on your skin may exacerbate your acne.
2. Oral Medications
Topical medicines are good for initial acne treatment. However, depending on your needs, the doctor may also prescribe you oral medications such as:
- Antibiotics
- Contraceptives or birth control pills (FDA has approved only three contraceptives for acne, so ensure you do not take them without a doctor’s prescription) (9)
- Accutane or Isotretinoin (mainly used for severe acne) (9)
- Spironolactone (mainly formulated for hypertension; but this medicine, in low doses, may help hormonal acne as it blocks androgen) (9)
3. Surgical Procedures
If both topical and oral medications fail to deliver results, you may opt for surgical procedures. Some of these procedures include:
- Electrosurgery: This is used for treating severe comedonal acne. In this procedure, electricity is used to destroy the tissue by dehydration, coagulation, or vaporization. There are two types of electrosurgery – high-frequency electrosurgery and electrocautery.
- Cryotherapy: In this procedure, the affected area is frozen for 20 seconds using liquid nitrogen or solid carbon dioxide. This eventually destroys the tissues in that area.
- Microdermabrasion: In this process, a device with a crystal head is rubbed on your skin to remove the top layer of your skin. This helps remove the comedones. Microdermabrasion is often used for treating acne scars.
4. Home Remedies
You may also take care of comedones at home by trying a few home remedies using simple and effective ingredients:
1. Tea Tree Oil
Five percent topical tea tree oil was found to be effective in treating mild to moderate acne (10).
You Will Need
- 2-3 drops of tea tree oil
- 1 teaspoon of any carrier oil (you may use jojoba, olive, sweet almond oils)
Method
- Mix the oils.
- Massage the mixture on the affected area.
- Leave it on for at least 20-30 minutes.
- Wash off.
How Often
2 times every day.
2. Witch Hazel
Witch hazel is commonly used for relieving inflammation and skin irritation(11). Though there is a lack of direct evidence, anecdotal evidence suggests that it has an astringent effect and can help minimize acne.
You Will Need
- A tablespoon of witch hazel
- Cotton pad
Method
- Wash your face and pat it dry.
- Saturate the cotton pad with witch hazel.
- Apply it as a toner to your skin.
- Let it dry.
- Follow it up with a non-comedogenic moisturizer.
How Often
Once every day (do not overuse as it may dry your skin out).
3. Charcoal And Clay Mask
Activated charcoal is works as an absorbent (12). It can eliminate dirt and sebum from your skin. The clay (especially bentonite clay) can soothe the skin and heal skin lesions (13).
You Will Need
- ½ teaspoon of activated charcoal powder
- 2 tablespoons of bentonite clay
- Water for mixing (you may use rosewater)
Method
- Mix the charcoal powder and the clay.
- Add water or rosewater as per the desired consistency and mix well.
- Spread the mixture on the affected area.
- Let it dry.
- Wash off with warm water.
- Follow up with a non-comedogenic moisturizer.
How Often
Not more than 2 times a week.
4. Apple Cider Vinegar
Though there is no direct evidence, anecdotal evidence suggests that the vinegar may work well as a toner. It also may act as an astringent and minimize skin pores, thus helping relieve acne. However, never use ACV without diluting it.
You Will Need
- ½ teaspoon of apple cider vinegar
- 2 tablespoons of distilled water (to dilute the ACV)
- Cotton pad
Method
- Wash your face and pat it dry.
- Mix the ACV and distilled water.
- Saturate the cotton pad with the mixture and apply it to your face as a toner.
- Let it dry and then apply a non-comedogenic moisturizer.
In addition to these treatment options, modifying your lifestyle also helps. In the following section, we have discussed the measures you can take to prevent comedonal acne.
Ways To Prevent Comedonal Acne
1. Wash Your Face Twice A Day
Use a mild cleanser or a cleanser containing salicylic acid to wash your face two times a day.
2. Use Non-comedogenic Products
Whether it is makeup or skincare, ensure you use non-comedogenic products. This way, your skin pores won’t get clogged, and you can prevent comedonal acne.
3. Remove Makeup Before Going To Bed
Removing makeup before hitting the bed allows your skin to breathe and heal itself while you sleep.
4. Keep Your Skin Accessories Clean
Clean your makeup applicators, brushes, and beauty blenders thoroughly after every use. Dirty accessories may accumulate germs and cause acne.
5. Follow A Healthy Diet
Following a daily skincare routine and a healthy lifestyle can help keep your skin clear to an extent. However, you may face breakouts from time to time, and you need to treat them properly. The methods outlined in this article can help. In case you have severe acne, it always is better to consult a doctor.
Reduce the intake of fried or processed foods, baked goodies, and sugary drinks. If possible, try to limit your milk intake. Instead, consume a lot of fresh produce and lean protein.
Comedonal acne is different from inflammatory acne caused by clogged pores, giving your skin a rough and bumpy appearance. While it is not a severe form of acne, the comedones may turn into inflammatory lesions if ignored. Therefore, following a regular skin care routine that includes anti-acne ingredients and products is crucial. You may use the remedies suggested in the article to soothe your skin and follow the tips to maintain a healthy lifestyle. However, consult a doctor to determine the best treatment method for your condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Accutane help treat comedonal acne?
Yes, it works for severe acne. Accutane is a form of vitamin A that reduces the amount of oil released by the skin’s oil glands. However, you shouldn’t take it without consulting your doctor.
Do closed comedones heal?
They can heal with proper treatment. However, if left untreated, they may turn into a serious issue.
Is comedonal acne hormonal?
Comedonal acne is mainly caused during the pre-teen years and is regulated by hormones. However, one may even experience them at a later point of their lives. Apart from hormonal changes, another major cause of this type of acne is poor skin hygiene. Certain products (shampoos, makeup, hair pomades) may also lead to comedonal acne as these contain chemicals and oils that may block the pores.
Sources
- Dairy Intake and Acne Vulgaris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 78,529 Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults, Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6115795/ - A pilot study to determine the short-term effects of a low glycemic load diet on hormonal markers of acne: A nonrandomized, parallel, controlled feeding trial, United States Department of Agriculture.
https://pubag.nal.usda.gov/catalog/590455 - Acne and smoking, Dermato Endocrinology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2835905/ - What is the Role of Benzoyl Peroxide Cleansers in Acne Management?, The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3016935/ - Clinical studies of 20% azelaic acid cream in the treatment of acne vulgaris. Comparison with vehicle and topical tretinoin., Acta Dermato- venereologica, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2528257 - Treatment of acne vulgaris with salicylic acid pads., Clinical Therapeutics, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1535287 - An update on the management of acne vulgaris, Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3047935/ - Tretinoin: A Review of Its Anti-inflammatory Properties in the Treatment of Acne, The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3225141/ - A Review of hormone-based therapies to treat adult acne vulgaris in women, International Journal of Women’s Dermatology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5419026/ - The efficacy of 5% topical tea tree oil gel in mild to moderate acne vulgaris: a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study., Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, and Leprology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17314442 - Witch-Hazel, ScienceDirect.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/witch-hazel - Formulation and Evaluation of Activated Charcoal Peel Off Mask, Research Gate, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333130903_FORMULATION_AND_EVALUATION_OF_ACTIVATED_CHARCOAL_PEEL_OFF_MASK
- Bentonite Clay as a Natural Remedy: A Brief Review, Iranian Journal of Public Health, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5632318/